“What’s your drink of choice?”, the famous line goes, and most people would definitely say “Tequila, please”. Tequila, a popular alcoholic beverage that originated in the southern part of North America a few centuries ago, is a unique cultural phenomenon the production of which bears as much importance as its exotic flavor and spheres of application, too.
So, why does this drink come from Mexico only, and what is the plant used to make tequila? In this material, the team of AI Plant Finder is going to tell you more about the hot spirit, its composition, and the authentic production process as it is.
The Blue Agave: The Main Component in Tequila Production
The place of tequila origin, the desert land of Mexico, has always been home to various peculiar creatures of faunal and floral origin. Having been the central source of nutrition, natives strived to find new flavors and forms to make their food experience richer and more advanced, and tequila is the result of such an experiment. But what cactus makes tequila in fact?
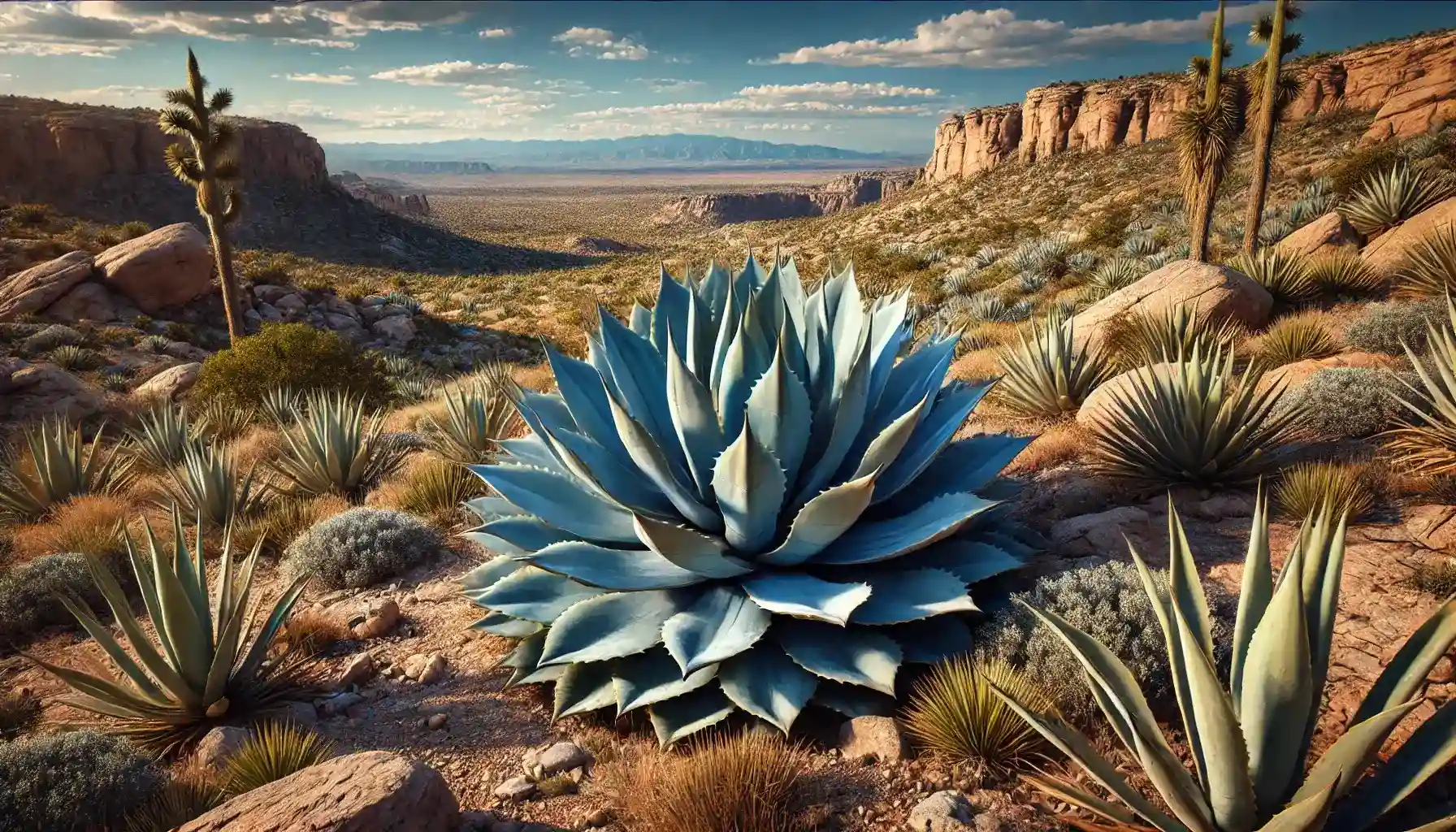
So as to create such a widely recognized drink, the Mexicans took the best out of “Weber Azul”, the cultivar of the blue agave scientifically known as Agave tequilana, a sophisticated succulent with a wild appearance but mild insides. Though all the traditional distilled beverages are made of local fruits, vegetables, grains, etc., it is tequila that attracts more and more alcohol lovers thanks to its exclusive composition and its alien aura as well.
What Should We Know About the Blue Agave?
The genus of Agave plants incorporates a wide range of succulents, with the blue agave being the most frequently used one. The appearance of such an unusual plant astonishes, for it features blue-green leaves of long and spiky patterns with sharp spines at the edges and a desired sugary pineapple at the center. Being native to some regions in Mexico, the plant may only prefer harsh, semi-arid climates with little to no temperature fluctuations and the volcanic soil of Jalisco and its surroundings.
To reach maturity, the blue agave needs to go through the process of development, which takes between six to eight years, as a rule. Nevertheless, however compact it may seem, this species is not considered the best plant for small-scale, non-commercial cultivation since it requires a lot of free space and proper environmental conditions to thrive efficiently and store as much sugar as needed.
How Is Tequila Made? Process Explained
The alcohol industry has its own rules and regulations that control the quality of the beverages and their flavor profiles. As prescribed, a drink should contain at least 51% blue agave to be considered tequila, with higher blue agave content indicating higher quality (which is quite obvious). All in all, to get a fine tequila, the plant should undergo a meticulous process to turn into a final hard liquor in the end.
Step 1. Harvest the Blue Agave.
Imagine having an entire field of what plant is used to make tequila. What should farmers do with their crops then? As soon as the blue agave is mature enough, it is time to harvest the plants. In general, it is the work of jimadors, skilled agave farmers, that involves cutting away the spiky leaves to reveal the heart of the plant, i.e., piña, which can weigh up to 200 lb. (90 kilograms) in total. This is exactly what they employ to make tequila from the blue agave plant.
Step 2. Cook the Piñas.
The piñas, that have been just harvested, are always carefully transported to the distillery to be heated so as to convert its inulin, i.e., the complex carbohydrates, into fermentable sugars. For 24 to 48 hours, one should cook piñas in special ovens called hornos with the slow-cooking approach in mind to achieve the preferred deeper flavor as a result.
Step 3. Crush and Extract.
As it can be easily deduced, the process of making alcohol requires sweet juice to be fermented and thoroughly prepared afterward. But first, one should extract the liquid by crushing the large piñas into smaller pieces and rolling over the roasted agaves to bring out the juice called aguamiel.
Step 4. Start Fermentation
The most challenging part always refers to fermentation, when the extracted juice should be transferred into fermentation tanks with yeast added to initiate the process. This, though, lasts a couple of days until all the sugars are converted into alcohol.
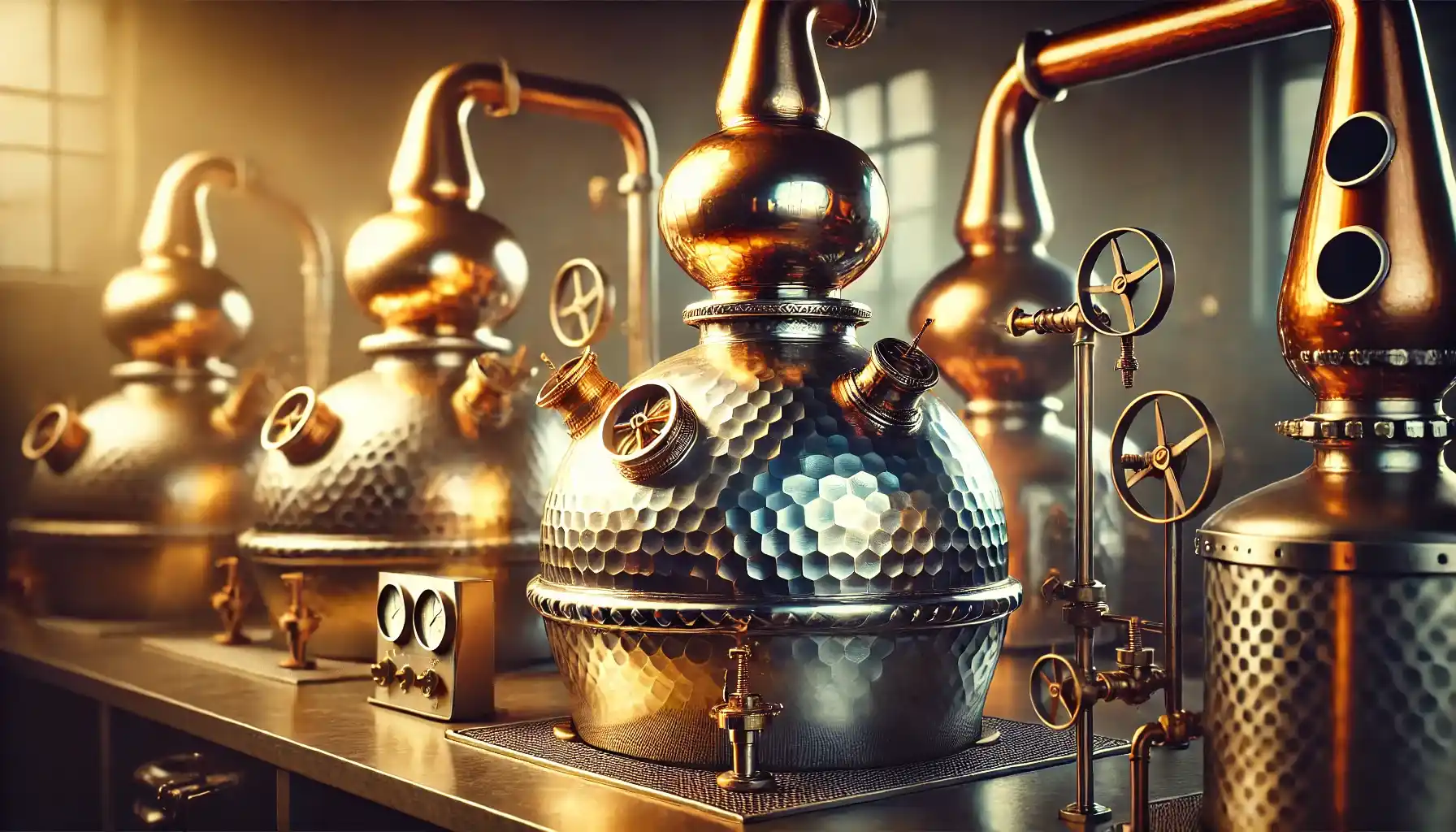
Step 5. Proceed with Distillation.
Generally speaking, the next step presupposes distillation when the fermented liquid turns into a cloudy substance (i.e., destrozamiento) and then converts into clear tequila in the end (rectificación) via special equipment. As such, the double distillation is aimed at purifying the alcohol and enhancing the concentration of flavors.
Step 6. Age Well (Though Optional)
It is not a call for action for you but the clear tequila to age in wooden barrels. In terms of maturation, tequila might fall into several groups, namely Blanco (bottled immediately after distillation), Reposado (aged for two months to less than a year), Añejo (aged for one to three years), and Extra Añejo (aged for three or more years).
Step 7. Add Flavorings and Bottle the Tequila.
After aging, the tequila may be finally filtered, enhanced with various additives, such as extracts, flavorings, and the like, diluted, and packed in the bottles at last. At this stage, tequila is ready for distribution and further consumption with pleasure, too.
Other Applications of Blue Agave
Though blue agave is mainly used in tequila production, its usability extends beyond the distillery. Since the sugar content of blue agave is high, some manufacturers praise the plant for the agave syrup derived from its sap. Those who opt for healthier options may surely consider agave syrup with its low glycemic index, which is particularly suitable for people managing their blood sugar levels.
Plants like the blue agave hide more than one can expect, yet searching for the truth behind each natural creation may require a lot of time. But how to explore the world of flora more smoothly and deeply? We could recommend dozens of platforms devoted to plantEd; however, there exists an app that has changed the game for good, i.e., AI Plant Finder.
Why AI Plant Finder?
AI Plant Finder is a popular plant-centered solution for those who are looking for answers but cannot figure out where to start. Want to learn more about habitat, plant care needs, growing conditions, and edibility potential? Cannot remember when to water your garden and how much light it requires? The AI Plant Finder can grant you the theoretical background powered by the real-life experience of other plant lovers from all over the world.
What you can do within the platform comes down to plant identification by photo, quick health check-up, water calculator, illuminance meter, and AI support connected to the database of more than 300,00 plant species available. Convenient and feature-rich, the app turns into your private garden log for you to keep track of your plants, manage their health, and promote the development of the environment around. Download the app now and let everyone know your garden is under control.
The blue agave plant is a universal resource with applications that extend beyond the production of tequila, though the latter covers its primary use. For Mexicans, as well as for the rest of the world, this hot spirit holds powers that can comfort and open a person, ease their pain, and induce feelings, too.
Nonetheless, one should always keep in mind that alcohol abuse is harmful to their health, so be sensible and consume it in reasonable doses.
AI Plant Finder Related Posts: